Have you ever wondered how your body communicates with itself to maintain balance and harmony? The human body is a highly complex and intricate system, relying on various components to function seamlessly. Among these are hormones, which act as chemical messengers, relaying instructions from one part of the body to another. These hormones are secreted by specific glands, each with its unique role and influence.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the seven main glands responsible for secreting hormones, exploring what they are, how they function, and why they’re vital for your overall health. Understanding these glands and their hormones can offer insight into the body’s incredible ability to self-regulate and adapt to both internal and external changes.
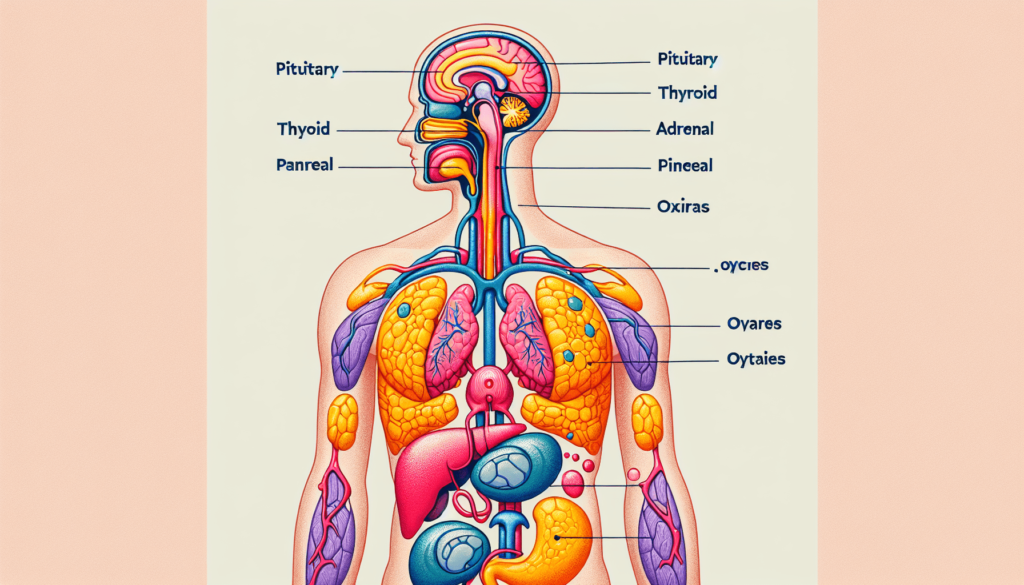
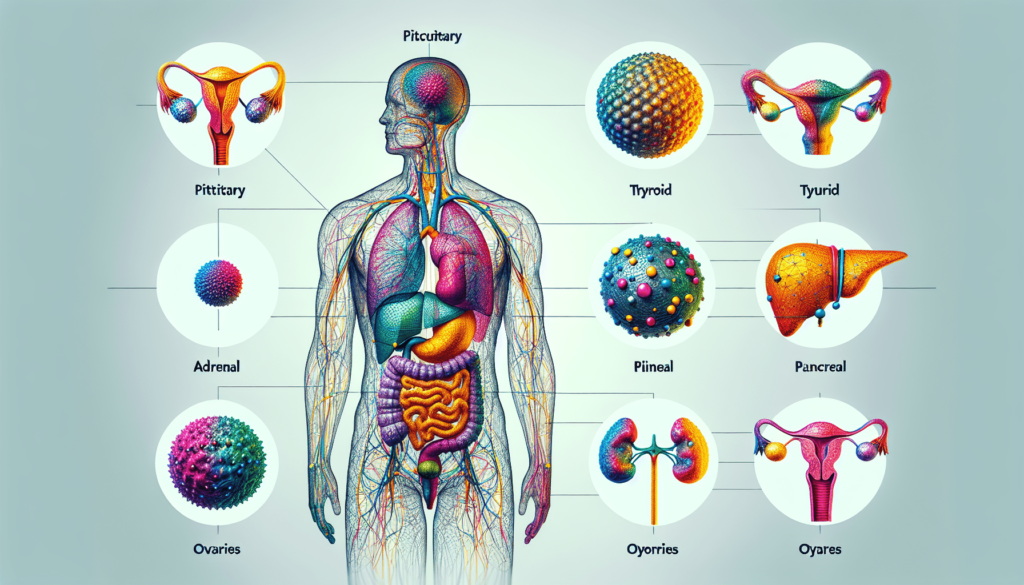
The Pituitary Gland: Master of the Orchestra
The pituitary gland, often dubbed the “master gland,” is centrally located in your brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating a multitude of bodily functions. Despite its small size, it orchestrates an array of hormonal activities by secreting hormones that influence other glands.
Hormones Produced by the Pituitary Gland
Table of Contents
- Growth Hormone (GH): Essential for growth and development, this hormone facilitates cell growth and regeneration.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): As the name suggests, it stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): It influences the adrenal glands to release cortisol, aiding in stress response and metabolism.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Both play crucial roles in regulating the reproductive processes.
- Prolactin: Promotes milk production in breastfeeding women.
Understanding these hormones helps you appreciate how the pituitary gland commands various bodily functions, affecting growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
The Thyroid Gland: Regulating Energy and Metabolism
The thyroid gland, shaped like a butterfly and located in your neck, is another essential player in your body’s hormone orchestra. It primarily controls your metabolism, which is the process by which your body converts food into energy.
Key Hormones of the Thyroid Gland
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): These hormones boost metabolic rate, influence heart and digestive function, muscle control, brain development, and bone maintenance.
Your thyroid’s ability to produce these hormones affects how your body utilizes energy and influences your weight, body temperature, and even mood.
The Parathyroid Glands: Guardians of Calcium
Nestled behind the thyroid gland are the tiny yet mighty parathyroid glands. Though small, they are crucial for maintaining the body’s calcium balance.
Hormone Secreted by the Parathyroid Glands
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): Regulates calcium levels in the blood, vital for proper functioning of the nervous and muscular systems.
These glands ensure your bones remain strong and your muscles and nerves function correctly by balancing calcium levels within your bloodstream.
The Adrenal Glands: Responding to Stress
Perched atop your kidneys, the adrenal glands are versatile players in hormone production. They are fundamental in controlling stress response and also affect metabolism and immune function.
Hormones from the Adrenal Glands
- Cortisol: Known as the “stress hormone,” it helps control mood, motivation, and fear. It also regulates several bodily functions during stress, including metabolism and immune response.
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine) and Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine): These increase heart rate, expand air passages of the lungs, and redistribute blood to muscles, preparing the body for a ‘fight or flight’ response.
These hormones are your body’s primary tools for handling stress, influencing everything from your heart rate to how you metabolize sugars.
The Pineal Gland: Setting the Rhythm
The pineal gland, nestled within the brain, is responsible for managing sleep patterns by regulating the production of melatonin, the sleep hormone.
Melatonin and Its Role
- Melatonin: Regulates sleep patterns, responding to darkness by inducing drowsiness and preparing the body for sleep.
Understanding melatonin’s role underscores the importance of sleep in maintaining overall health and the influence of modern life on sleep quality due to light exposure.
The Pancreas: Balancing Sugar Levels
Located in the abdomen, the pancreas has both digestive and hormonal functions. It plays an integral role in regulating blood sugar levels through insulin and glucagon production.
Key Hormones of the Pancreas
- Insulin: Helps lower blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake by the cells.
- Glucagon: Works in opposition to insulin by raising blood sugar levels when they fall too low, ensuring homeostasis.
The pancreas’ ability to maintain sugar levels is crucial for providing energy to cells while preventing conditions like diabetes.
The Gonads: Reproductive Health and Beyond
The gonads, which include the ovaries in females and the testes in males, are essential for reproductive health. They also impact secondary sexual characteristics and behaviors.
Hormones Secreted by the Gonads
In Females (Ovaries)
- Estrogen and Progesterone: Maintain reproductive health, regulate the menstrual cycle, and support pregnancy.
In Males (Testes)
- Testosterone: Influences male physical characteristics and fertility.
These hormones not only determine reproductive functionality but also affect broader aspects such as bone density, muscle strength, and mood.
The Interplay Between Hormones
Every hormone in your body has a specific function, yet it’s their interaction that truly keeps the system in balance. When one gland or hormone is out of kilter, it can set off a chain reaction affecting others. Think of it as a symphony, where each instrument plays a crucial role toward a harmonious concert.
Metabolism and Energy Balance
Hormones like insulin and thyroid hormones play pivotal roles in regulating metabolism and energy expenditure. When they operate in harmony, energy is efficiently managed, influencing weight and overall vitality.
Stress and Emotional Well-being
Adrenal hormones like cortisol work in tandem with other hormones to guide your body through stress. Their balance impacts not only your physical response but also emotional well-being.
Growth and Development
Growth hormone and sex hormones coordinate to manage growth patterns from infancy through adulthood, determining height, muscle mass, and more.
Reproductive Processes
The synchronization between luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and sex hormones regulates reproductive cycles and fertility, affecting both males and females.
Maintaining Hormonal Health
Given the role these hormones play in nearly every function of your body, maintaining their balance is crucial. Unhealthy diets, chronic stress, lack of exercise, and poor sleep can all disrupt this delicate balance.
Tips for Hormonal Health
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate a mix of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, as well as vitamins and minerals.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity to boost metabolism and regulate hormones.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure quality sleep by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
- Stress Reduction: Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques to help manage stress levels.
- Regular Check-ups: Periodically consult healthcare providers to monitor hormonal health.
Conclusion
With this newfound understanding of the seven glands that secrete hormones, you’re well-equipped to appreciate them as the unsung heroes of your body’s daily symphony. They’re the backstage characters ensuring every system runs smoothly, from growth to metabolism, stress management to reproduction. By acknowledging their roles and tending to your body’s needs, you’re taking a proactive approach toward better health and overall well-being. So, here’s to these small yet mighty powerhouses, working tirelessly to keep your body balanced, healthy, and thriving.





